Advertisement
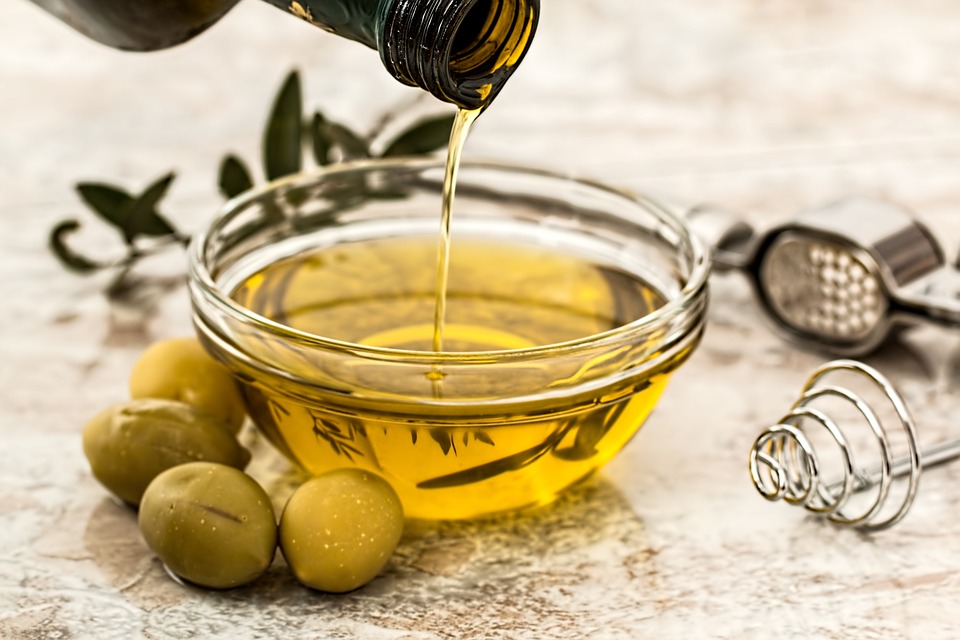
Olive oil is a plant-based cooking oil made from the fruits of the olive tree. It’s made by pressing olives into a paste and mixed with water. This mixture is pressed again, after which the pulp is removed to make olive oil. This oil has long been considered the healthiest cooking oil because of its various benefits.
More recently, another cooking oil has made its way into people’s kitchens: Avocado oil. Avocado oil is made in pretty much the same way as olive oil, except the fruit’s seed and pit are removed first. The flesh is ground to a paste and churned to extract the oil. The oil then goes through a final filtration process to remove leftover pulp.
Both avocado oil and olive oil are rich in nutrients and powerful compounds. Both oils also offer many benefits. But is one oil better than the other? Read on to find out.
Nutrition facts and health benefits
Fat content is generally where most cooking oils differ. But that’s not the case with olive and avocado oils. They both contain high amounts of healthy monounsaturated fats, with only slight differences.
Oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid, makes up the bulk of the healthy fats found in both olive and avocado oils. Its main health benefits include lower cholesterol levels, reduced inflammation and better heart conditions.
Both olive and avocado oils are also low in polyunsaturated fats. Though these fats aren’t as bad for your health as trans or saturated fats, they can still be stored in the body over time, leading to inflammation.
When it comes to antioxidants, however, olive oil wins over avocado oil because it has more vitamin E. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Olive oil and avocado oil contain other antioxidants, such as carotenoids. Carotenoids are a group of more than 750 naturally occurring pigments. They are responsible for the brightly colored peels of many fruits and vegetables. Two of the most common carotenoids found in foods are alpha- and beta-carotene.
Gram for gram, however, olive oil contains more beta-carotene than avocado oil. Beta-carotene, the red-orange pigment in carrots and sweet potatoes, is a powerful antioxidant capable of reducing inflammation and protecting the brain from oxidative stress, which has been associated with brain aging.
On the other hand, avocado oil contains more alpha-carotene than olive oil. High blood levels of alpha-carotene are associated with a longer life and a lower risk of dying from cardiovascular disease.
Furthermore, both olive and avocado oils contain significant amounts of lutein and zeaxanthin. These powerful antioxidants are the only carotenoids that accumulate in the retina, the thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. In particular, they accumulate in the central region of the retina called the macula.
The macula is essential for vision. Lutein and zeaxanthin work by protecting the macula from harmful free radicals. It is thought that low levels of lutein and zeaxanthin in the macula can lead to poor vision over time.
Taste
Generally speaking, most people don’t think about the flavor of their cooking oils mainly because vegetable oils like canola oil, which most people use, are flavorless. But flavor matters when it comes to clean, healthy oils like olive and avocado oils.
For starters, olive oil can taste mildly bitter. The intensity of the oil’s naturally bitter flavor varies depending on the ripeness of the olives used. Oil extracted from ripe olives is less bitter compared to oil extracted from greener olives.
Unrefined olive oil also has a mild vegetal flavor. You might also note a peppery taste at the back of your throat upon swallowing the oil. The oil is said to be of high quality if the peppery taste makes you cough.
Meanwhile, clean, unrefined avocado oil tastes grassy and is reminiscent of mushrooms.
Smoke point and uses in cooking
Avocado oil has a very high smoke point, which is usually between 480 to 520 degrees Fahrenheit (270 degrees Celsius). Therefore, avocado oil is great for high-heat cooking. Things like baking, roasting, searing and grilling all work well with avocado oil.
On the other hand, olive oil’s smoke point varies depending on the grade of the oil and the processing it had gone through. Unrefined olive oil, such as extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO), has a low smoke point of about 220 degrees Fahrenheit (105 degrees Celsius). As such, olive oil is best for short sautés or for drizzling on salads, pasta dishes and meats.
Knowing the smoking point of each oil is important because oils lose most of their nutrients when heated to their smoking points. Heating oils to their smoking points also results in the formation of toxic compounds, some of which can lead to cancer.
Both olive oil and avocado oil contain similar levels of healthy versus unhealthy fats. But when it comes to their anti-inflammatory properties or antioxidant content, olive oil may be the better option. Just make sure to buy the unrefined, extra-virgin kind. But if you’re frying, grilling or roasting at high temperatures, use avocado oil.
Sources:
Advertisements