Advertisement
When it comes to beverages, there’s nothing quite as comforting as a hot cup of cocoa.
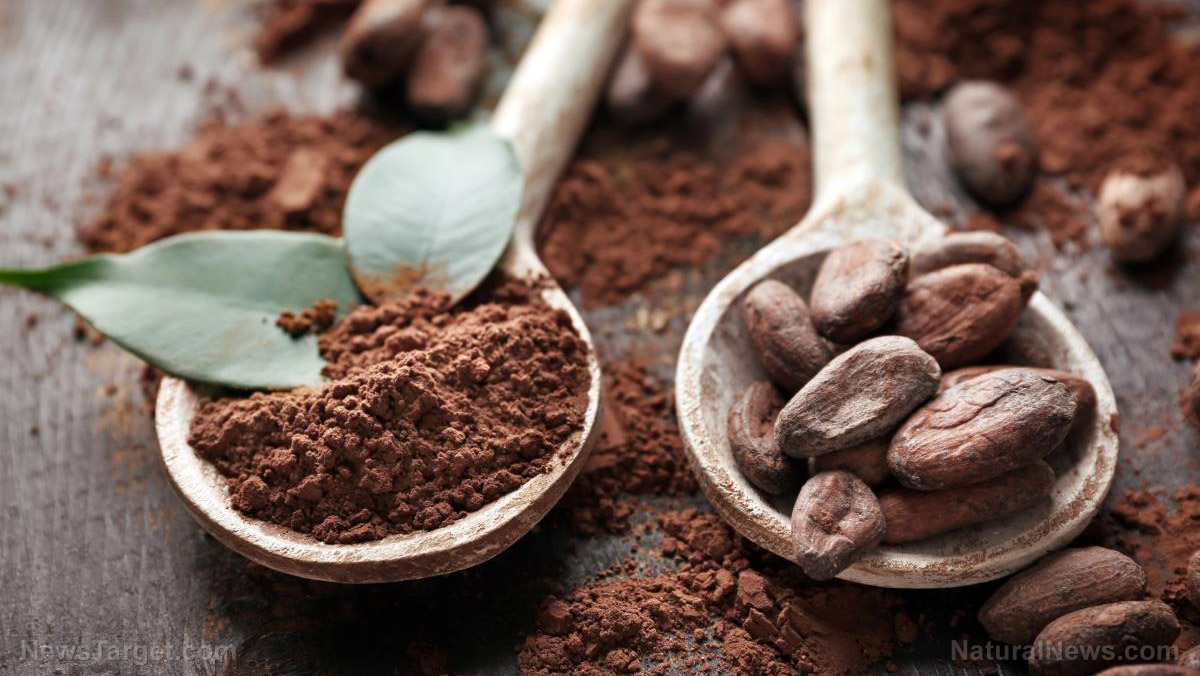
Derived from the beans of the cacao plant (Theobroma cacao) and first cultivated by the Aztec and Maya civilizations of Central America, cocoa as we know it, started out as a bitter beverage called “cacahuatl” that was shared during religious ceremonies.
The drink soon found its way to Europe, thanks to the Spanish conquistadors who brought home with them their newfound knowledge regarding the cacao plant, its precious beans, and how to process them.
From there, the drink took a life of its own: mixed with spices and sweeteners, it was hailed by the upper classes as a delicious and healthy beverage, and was even marketed as a powerful aphrodisiac.
There’s more to cocoa than just being a sweet and comforting drink, however, it’s actually packed full of vitamins and minerals.
According to experts, 100 grams or 6 tablespoons of unsweetened cocoa powder contains the following nutrients:
- 57.9 grams of carbohydrates
- 13.7 grams of fat
- 19.6 grams of protein
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) – 14 percent Daily Value (DV)
- Niacin (Vitamin B3) – 11 percent DV
- Folate (Vitamin B9) – 8 percent DV
- Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) – 6 percent DV
- Thiamin (Vitamin B1) – 5 percent DV
- Manganese – 192 percent DV
- Copper – 189 percent DV
- Magnesium – 125 percent DV
- Iron – 7 percent DV
- Phosphorus – 73 percent DV
- Zinc – 45 percent DV
- Potassium – 44 percent DV
- Selenium – 20 percent DV
- Calcium – 13 percent DV
Where cocoa shines, however, is in its antioxidant content.
As noted in a study published in the journal Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, cocoa contains flavonoids such as catechins, epicatechins, and procyanidins — all of which are linked to several important health benefits.
Cocoa can help reduce high blood pressure
The next time you feel like your blood pressure is shooting up, go to the kitchen and make yourself a cup of cocoa.
Cocoa, according to researchers, may be able to help lower blood pressure in certain individuals.
This reduction in blood pressure is caused by flavonols, which, as noted in a study published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, helps improve the levels of nitric oxide in the blood.
Nitric oxide causes blood vessels to relax and dilate, thus helping to lower your blood pressure.
Aside from flavonols, cacao also has other antioxidants, namely catechins and anthocyanins, which help promote healthy cardiovascular function by maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Cocoa may help improve your cognitive function and mood
Need more brainpower? Grab a cup of hot cocoa!
This is because cocoa is packed full of antioxidant compounds that can reduce your risk of neurodegenerative diseases by supporting neuron production and brain function as well as by improving blood flow to the brain.
In addition to helping improve your cognitive function, the antioxidants in cocoa may also exert some positive effects on your mood according to another study which noted the absorption and accumulation of flavonoids in the brain regions involved in learning and memory.
As detailed in the research, this accumulation of antioxidants helps reduce stress levels, as well as improves calmness, contentment and overall psychological well-being.
Also, cacao is considered by experts to be one of the best plant-based sources of magnesium, a mineral that helps turn glucose into energy, which then enables your brain to work with laser-sharp focus.
Cocoa may help in safe and sensible weight management
While it may seem counterintuitive, research suggests that consuming a little dark chocolate may play a role in controlling your appetite, which in turn could help you manage your weight.
According to neuroscientist Will Clower, this is because consuming a little dark chocolate — and by extension dark cocoa — before or after meals triggers the release of hormones that signal to the brain that you’re already full.
Furthermore, as noted in an article published in the journal Frontiers in Pharmacology, chocolate actually promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which, in turn, results in healthy metabolism.
Cocoa may help prevent the development and spread of certain types of cancers
If you want to guard themselves from the wrath of cancer, you may want to indulge in some hot cocoa — the antioxidants in cocoa are some of the most potent, after all.
In fact, according to a study published in the Journal of the American Society of Hypertension, people who constantly snack on dark chocolate develop fewer cancers than those who don’t consume them — an effect believed to be caused by the antioxidants epicatechin and quercetin.
In addition, test-tube studies on cocoa’s components show that not only do the compounds have antioxidant effects, they are also capable of inhibiting malignant cell growth, induce apoptosis or death in cancer cells and even help prevent their spread.
Animal studies regarding cocoa-rich diets and the use of cocoa extracts too have seen positive results, with some studies even noting their capability to reduce breast, pancreatic, prostate, liver and colon cancers and even leukemia.
Researchers note, however, that while the limited studies in humans are promising, more research is needed in order to confirm cocoa’s potential role in cancer prevention.
Cacao can help provide relief in people with asthma
Cocoa, according to preliminary research, may be beneficial for asthmatic people as it contains the compounds theobromine and theophylline which have properties that can offer relief to people suffering from asthma.
Theobromine, for instance, is similar to caffeine and may help with persistent coughing, while theophylline helps the lungs dilate, as well as relaxes the airways and decreases inflammation.
Take note, however, that these findings have not yet been clinically tested in humans, and that further research is needed in order to see if cocoa can be safely used as a treatment option in conjunction with other anti-asthmatic drugs.
Cocoa can help nourish and protect the skin
If you’re looking for ways to improve and nourish skin, you may benefit from a cup of hot cocoa.
According to experts from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, this is because cocoa is packed full of essential minerals that are beneficial to the skin.
These minerals include manganese, which supports the production of collagen which helps keep the skin looking young and healthy. Another mineral present in cocoa is calcium which helps repair and maintain the body’s skin cells.
Aside from these minerals, several earlier studies have also found that cocoa contains high levels of antioxidants such as polyphenols, procyanidin, and flavonoids which help reduce the appearance of aging and keep the skin looking refreshed and revitalized.
These antioxidants, research says, may also help protect skin from the powerful ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun.
Cocoa may help improve some symptoms related to Type 2 Diabetes
Despite its sugar content, moderate consumption of cocoa has some surprising effects that diabetics can benefit from.
According to a review published in the journal Antioxidants, the flavonoids present in cocoa possess properties that can help people who have diabetes. These include enhancing insulin secretion, improving insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues, exerting a lipid-lowering effect and preventing the oxidative and inflammatory damages associated with the disease.
A separate study, meanwhile, even found that a higher intake of flavonols such as the ones present in cocoa can help lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Cocoa may be good for maintaining optimal gut health
Aside from being tasty, cacao is also good for your tummy. This is according to researchers from the University of Reading in the United Kingdom, who measured higher levels of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species in the intestines of people who drank high-cocoa chocolate milk for 4 weeks.
These bacterial groups, the researchers said, are known for their ability to prevent the growth of pathogenic organisms.
In addition, the same team also noted that cocoa effectively hampered the growth of Clostridium histolyticum, a species of bacteria that is usually present in the guts of individuals with inflammatory bowel diseases.
Cocoa is one of the world’s most potent food items. However, those who are looking to increase their intake should consider getting natural and organic cocoa powder that has not been alkalized or processed through the Dutch method, since that strips cocoa of its flavonoids.
Also, despite the benefits one gets from cocoa flavonoids however, experts say it’s best to consume cocoa in moderation, adding that one still has to factor in the amount of fat and sugar present in it.
For more stories about the healing power of foods, head over to SuperFoods.news.
Sources:
Advertisements