Advertisement
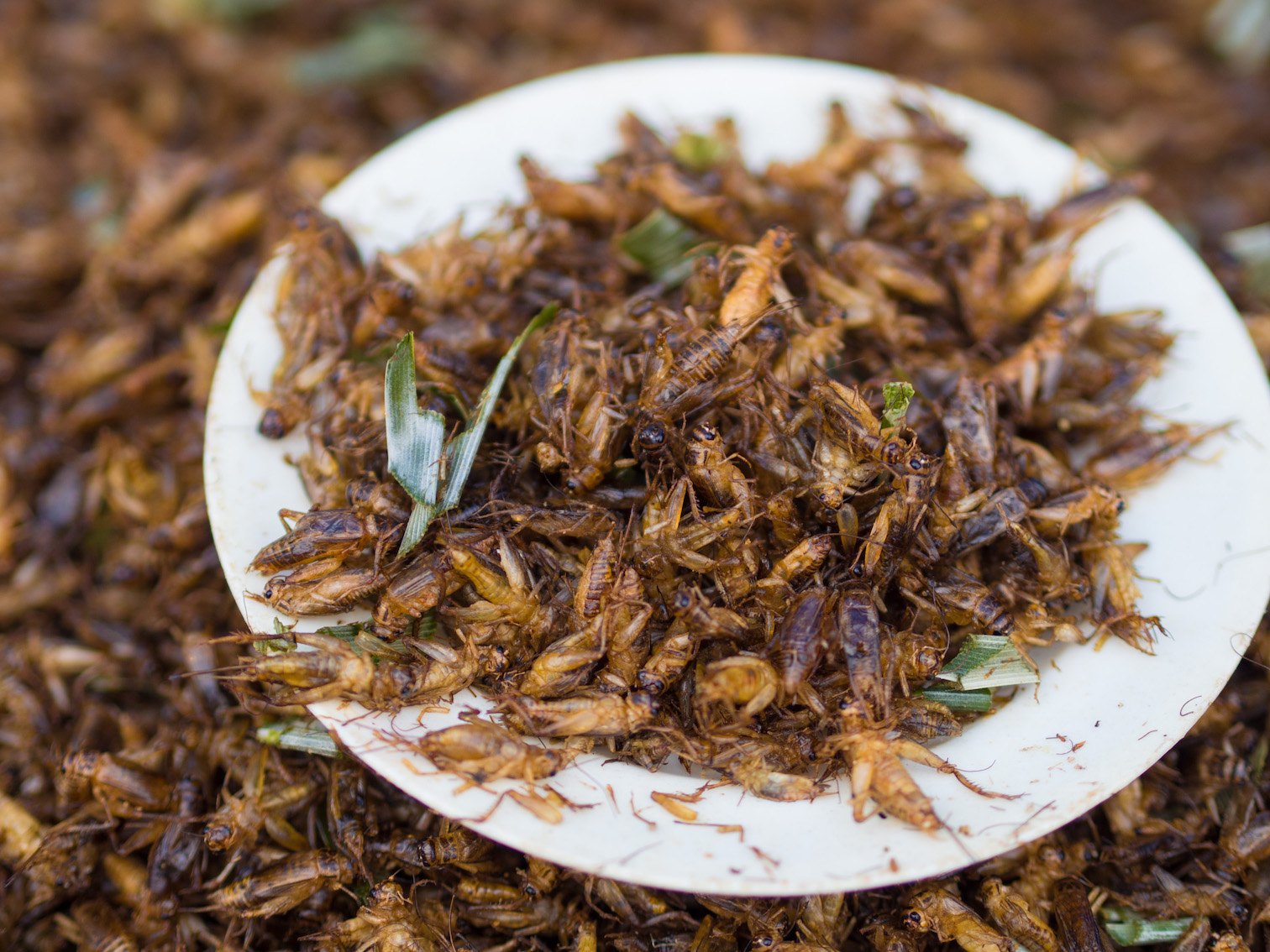
Game shows like Fear Factor dare challengers to complete stunts, some of which include eating live insects. Tourists in foreign countries would challenge themselves to try the local cuisine, which, in some cases, include unusual ingredients like edible insects.
Today, people are more open-minded when it comes to trying unique foods. Experts even suggest that, one day, people will think about edible insects as normal ingredients, just like fruits and vegetables.
America isn’t new to food trends. In the 1950s, Italian food and pizza took the country by storm. Now, over 40 percent of Americans eat pizza at least once a week.
In the 1970s, Mexican cuisine introduced Americans to new dishes like enchiladas, refried beans, salsa, tacos and tortillas. Two decades later, Japanese foods like sushi entered the picture. These days, you can get sushi in most modern restaurants or in some grocery stores.
With enough coaxing, experts believe that consumers will soon regard edible insects as a permanent addition to their regular diets.
Here are seven reasons to consider edible insects as a source of dietary protein.
Edible insects can contribute to food security
The United Nations (UN) reports that by 2050, the world’s population will skyrocket to 9.7 billion. However, feeding that many people requires the production of twice as much food than is currently being produced.
Unfortunately, there also isn’t enough arable land to accomplish this.
In 2013, the UN presented a report on eating edible insects. Turning to edible insects can help with food security, especially since one-third of the planet’s arable land is already used for livestock. This has also caused ongoing problems with deforestation and the use of too much of the planet’s water resources.
Edible insects offer high-quality protein
Insect protein is also worth a second look because it’s a natural source of high-quality dietary protein.
Beef is only made up of 29 percent protein, but crickets are made up of 69 percent protein. Even better, crickets contain nine essential amino acids and nutrients like calcium, iron, magnesium, potassium, sodium, vitamin B12 and zinc.
Cricket flour also contains more calcium than milk, and, surprisingly, more iron than leafy greens like spinach.
Many cultures consume insects
At least 80 percent of the world’s population already consumes insects. Westerners who have visited Southeast Asia have seen how locals regularly enjoy edible insects like toasted crickets.
In Mexico, yellow mealworms are used to make tortillas. In South America, people eat fire ants, while in Africa, locals consider beetle larvae a delicacy.
In a 2017 study, Australian consumers helped researchers from the University of Adelaide realize the potential of edible insects as a food industry.
Through a preliminary online survey of 820 Australian consumers, the researchers found that at least 20 percent of the survey takers had already tasted edible insects. Among the participants, 46 percent were willing to try a cookie made from insect flour.
For the study, scientists tested consumer attitudes at Adelaide Central Market by offering them unusual but edible items like roasted crickets and ants, mealworm cookies and cricket energy bars.
Associate Professor Kerry Wilkinson, one of the study authors, believes that edible insects may be the key to ensuring global food security. But issues like this can only be addressed by encouraging a positive shift in food consumption habits, especially when it comes to meat.
Edible insects require fewer resources than livestock
There are more than 2,000 types of edible insects, including:
- Ants
- Beetles
- Caterpillars
- Cicadas
- Crickets
- Dragonflies
- Grasshoppers
- Leaf and planthoppers
- Locusts
- Scale insects
- Termites
- True bugs
- Wasps
Insects have a high feed-conversion efficiency rate, a factor measured in kg of feed per kg of weight gain. This rate determines an animal’s capacity to convert feed into increased body mass.
Additionally, insects require less water than livestock, such as cattle, goats, poultry or sheep.
For example, 100 gallons of water are needed to produce only six grams of beef protein and 18 grams of chicken protein. These are equivalent to at least 238 grams of cricket protein. If a family of four consumes food made with crickets even just once a week for a year, it would help save a total of 650,000 liters of water.
Farming edible insects require less space than other foods sources
According to the UN, at least 68 percent of the world’s population will live in cities by 2050.
Unlike cattle, insects require less space, and they can be raised in warehouses and other urban buildings.
Edible insects can also be used as animal feed
More than 50 percent of the fish consumed around the world are farmed. High-quality insect protein can be used as fishmeal because insects are a natural food source for fish.
Additionally, insects are a natural food source for poultry. In fact, they’re considered superfoods for poultry because the exoskeletons of insects contain a carbohydrate known as chitin.
Chitin naturally strengthens the immune system of poultry, eliminating the need for antibiotics that can cause negative side effects as they go up the food chain.
Farming edible insects can be profitable
Investors predict that the global market for edible insects will reach $1.53 billion in 2021.
This is good news since:
- Insect farming offers a high demand that easily exceeds its supply.
- Insect farming can be done in small buildings with a minimum number of employees.
- Insects have a high reproduction rate.
- Insects are easy to manage and transport.
If you’re curious about products made from edible insects, check out items from two insect farming companies, Chapul and EXO. Both companies are now manufacturing protein bars made with insects like crickets, grasshoppers and mealworms. You can buy them at health food stores, grocery stores, online or at airport kiosks.
You can also experiment with flour made from crickets and mealworms. Try baking biscuits, bread, cookies, muffins and other desserts using insect-based flour. Alternatively, you can make pasta, smoothies or soups using it.
The sky’s the limit if you open your mind and try edible insects for a more sustainable source of dietary protein.
Sources:
Advertisements