Advertisement
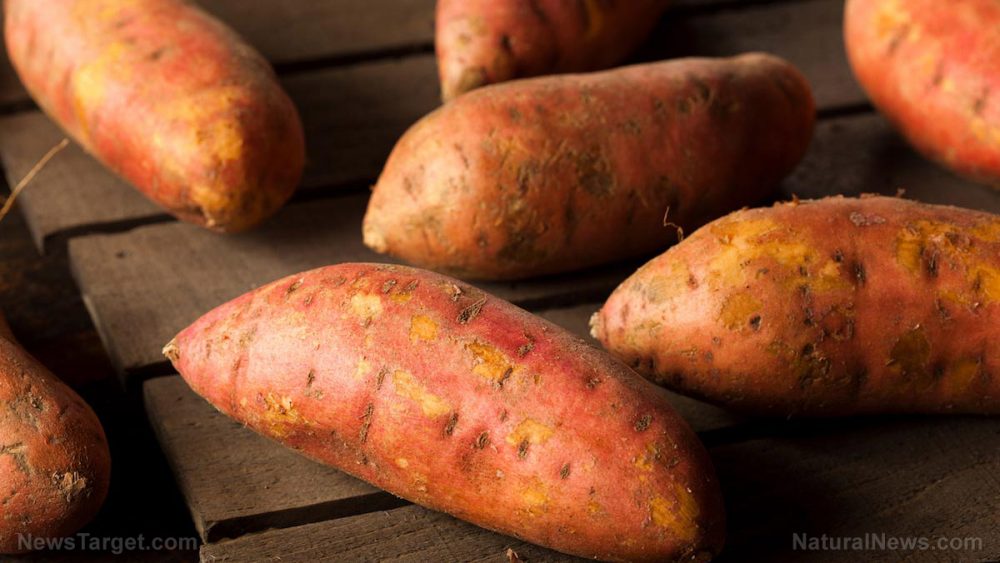
Sweet potatoes may not be as popular as regular potatoes, which is too bad — since they’re packed with vitamins and minerals. One cup of sweet potatoes can provide more than 100 percent of the daily value of vitamin A. It’s also rich in vitamin C, dietary fiber, and manganese. Both purple and orange varieties contain antioxidants that can protect the body from damage caused by free radicals.
Eating sweet potatoes is beneficial for your health
Sweet potatoes are brimming with micronutrients and antioxidants — making them useful to your health. Below is a list of reasons why you should incorporate sweet potatoes into your diet.
They improve brain function
The purple variety of sweet potato contains anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have revealed that anthocyanins are effective at improving cognitive function. Moreover, the results suggest that purple yams can help protect against memory loss. Antioxidants from the purple variety safeguard the brain against damage from free radicals and inflammation.
They aid digestion
Sweet potatoes are rich in dietary fiber. This macronutrient prevents constipation, diarrhea, and bloating by adding bulk and drawing water to the stool. In addition, fiber keeps a healthy balance in the gut by promoting the growth of good bacteria.
They slow down aging
The beta-carotene in orange sweet potatoes can help reduce damage caused by prolonged sun exposure. This is especially true for people diagnosed with erythropoietic protoporphyria and other photosensitive diseases. Sweet potatoes also contain antioxidants that protect against free radical damage. Free radicals are not only linked to diseases but also premature aging.
They boost the immune system
Orange and purple sweet potatoes are loaded with a good number of antioxidants that help protect the body from harmful molecules that cause inflammation and damage DNA. This, in turn, protects the body from chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease.
They can prevent cancer
Eating sweet potatoes can help protect against various types of cancers. The compounds in sweet potatoes restrict the development of cancer cells. Test tube studies have shown that anthocyanins can prevent cancers in the bladder, breast, colon, and stomach.
They lower blood sugar
Despite its relatively high glycemic index, studies have shown that the regular intake of sweet potatoes can help lower blood sugar, thanks to the presence of dietary fiber. While fiber falls under carbohydrates, it is digested differently, compared to starchy and sugary forms of carbohydrates. Interestingly, insulin doesn’t process fiber (unlike other types which get turned into glucose), and it only passes through the digestive tract.
They promote healthy vision
Orange sweet potatoes are rich in a compound called beta-carotene, an antioxidant which transforms into vitamin A in the body. Adequate intake of vitamin A promotes eye health. Conversely, deficiencies in vitamin A have been linked to a particular type of blindness called xerophthalmia.
Sweet potatoes are easy to incorporate into your everyday meals. They are best prepared boiled but can also be baked, roasted, or steamed — they can even replace other carbohydrates such as rice, potatoes, and toast. (Related: Understanding the phytochemical and nutrient content of sweet potato flours from Vietnam.)
For more stories and information about sweet potatoes, visit Food.news.
Sources include:
Advertisements