Method review for increasing consumption of vegetables in early childhood
03/21/2018 / By Michelle Simmons / Comments
Views

Advertisement
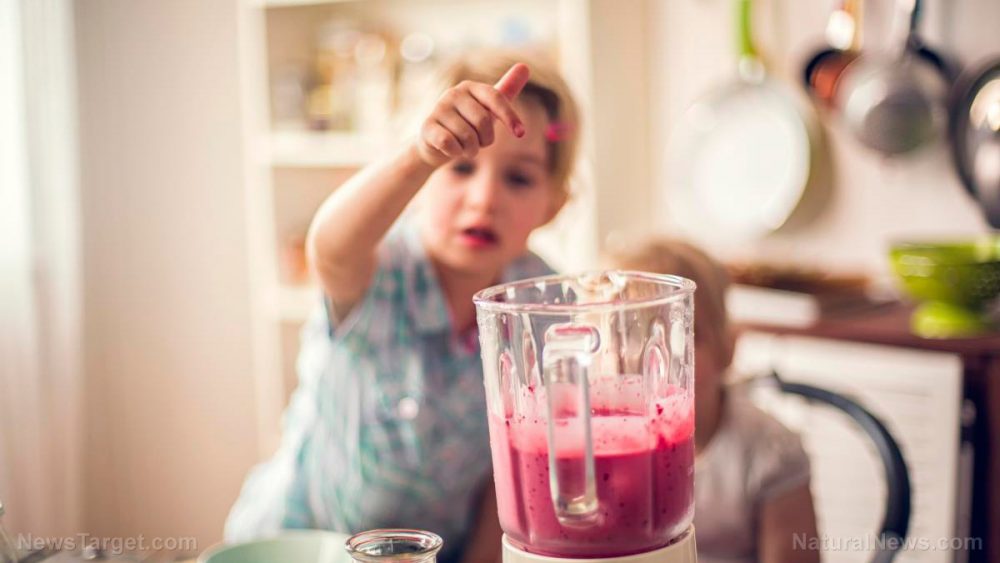
A review of studies published in the journal Current Nutrition Reports looked at the possible methods for increasing vegetable consumption in early childhood, and offered advice for practitioners.
- Researchers reviewed studies that used different methods to increase vegetable consumption in children aged two to five years.
- They used the key terms “child vegetable consumption”, “intervention”, “modelling”, “reward”, “flavor-flavor, “flavor-nutrient”, “repeated exposure”, “messy play”, and “tactile play” for selecting studies to be reviewed in the search engines Web of Science and PubMed.
- Their findings showed that repeated exposure is likely the most effective method of increasing vegetable consumption in early childhood.
- Pairing repeated exposure with other methods, such as modeling by peers or parents, may be more effective.
- Modeling methods may be most successful as part of mixed-methods interventions.
- Non-food rewards method is likely to be effective for achieving the tastings needed for children to like and accept vegetables.
- More research is needed to identify whether pairing vegetables — particularly bitter vegetables, or particularly bitter-sensitive or fussy children — with liked flavors are effective for increasing children’s vegetable consumption.
- Nutrition education may also be effective for preschoolers, but more exploration is needed for this method.
- The review authors suggested that practitioners may want to focus their advice to parents around techniques, such as repeated exposure, modeling, and non-food rewards.
- They also suggested that practitioners should examine how nutrition education programs might be implemented in an effective method for preschool children.
In conclusion, the review suggested that repeated exposure is the most effective method for increasing children’s vegetable intake which may benefit from being combined with modelling by peers or parents or with non-food rewards.
For the full text of the study, go to this link.
Journal Reference
Holley CE, Farrow C, Haycraft E. A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW OF METHODS FOR INCREASING VEGETABLE CONSUMPTION IN EARLY CHILDHOOD. Current Nutrition Reports. 2017; 6(2): 157-170. DOI: 10.1007/s13668-017-0202-1
Tagged Under:
bitter sensitive, child, children, early childhood, fussy eaters, intervention, non-food reward, nutrition, parent modeling, peer modeling, repeated exposure, vegetable consumption, vegetable intake, vegetables
100% Fresh Food News, Right at Your Fingertips!
Find out everything you need to know about clean and healthy eating when you sign up for our FREE email newsletter. Receive the latest news on all the top superfoods, recipes, natural remedies, diets, food tips, and more!
Your privacy is protected. Subscription confirmation required.
Related Articles
Advertisements